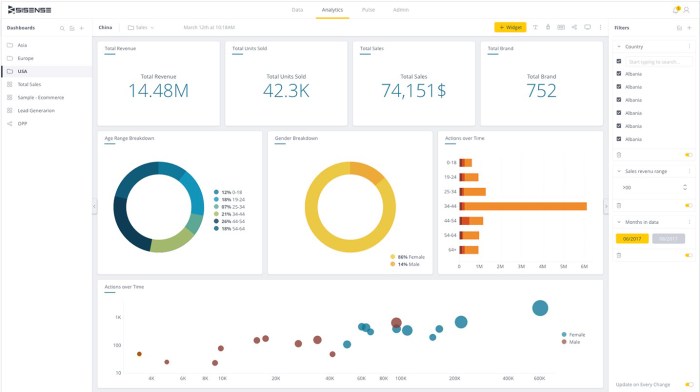
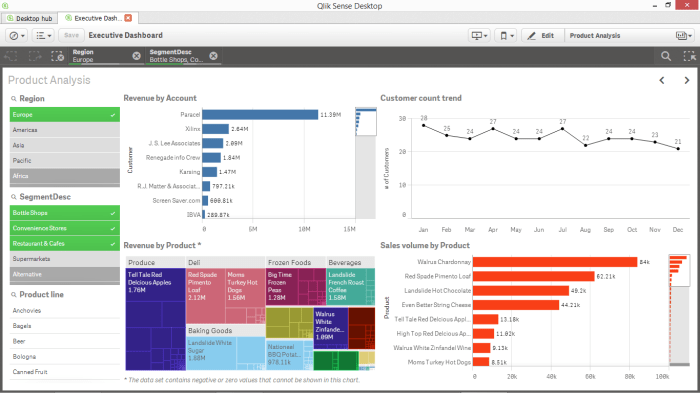
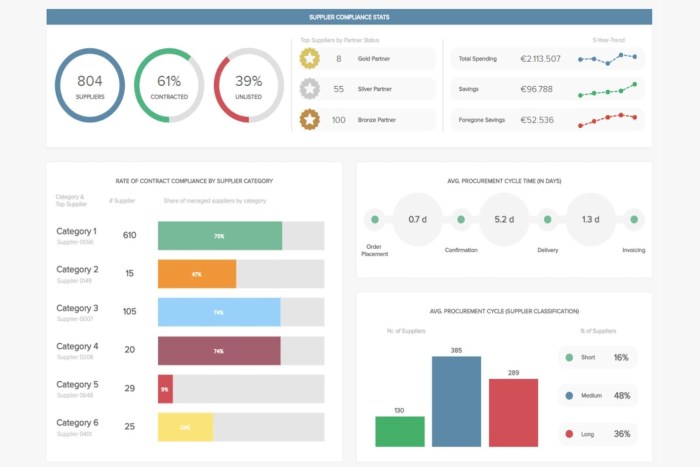
Business intelligence and data analytics career opportunities are booming! The demand for skilled professionals in this field is skyrocketing across diverse industries, from tech giants to healthcare providers. This isn’t just about crunching numbers; it’s about uncovering hidden insights, driving strategic decisions, and shaping the future of businesses worldwide. This guide dives deep into the exciting world of BI and DA, exploring career paths, required skills, and the strategies you need to land your dream job.
We’ll break down the current job market, detailing salary expectations, fastest-growing sectors, and geographical variations in compensation. You’ll learn the essential technical skills (think SQL, Python, R, Tableau) and the crucial soft skills needed to thrive. We’ll map out various career paths, from Data Analyst to Data Scientist, and show you how to navigate your career progression. Plus, we’ll cover the future of the field, including the impact of AI and machine learning, and provide actionable job search strategies to help you succeed.
Job Market Overview

The Business Intelligence (BI) and Data Analytics (DA) fields are experiencing explosive growth, driven by the increasing reliance on data-driven decision-making across all sectors. Businesses of all sizes recognize the value of extracting insights from their data to improve efficiency, optimize operations, and gain a competitive edge. This translates into a robust and consistently expanding job market for skilled professionals.The demand for BI and DA professionals is exceptionally high, with numerous opportunities available across various industries.
Companies are actively seeking individuals with strong analytical skills, technical proficiency, and the ability to communicate complex data insights effectively to both technical and non-technical audiences. This isn’t just a trend; it’s a fundamental shift in how businesses operate.
Fastest-Growing Sectors for BI and DA Professionals, Business intelligence and data analytics career opportunities
Several sectors are experiencing particularly rapid growth in their demand for BI and DA specialists. These industries are heavily reliant on data analysis for strategic decision-making and operational optimization. The competitive landscape necessitates a deep understanding of data trends and patterns.
- Technology: The tech industry, unsurprisingly, is a leading employer, with companies constantly seeking analysts to improve product development, marketing strategies, and customer experience.
- Finance: Financial institutions heavily rely on BI and DA for risk management, fraud detection, algorithmic trading, and investment strategies. The need for sophisticated data analysis is paramount.
- Healthcare: The healthcare sector is undergoing a digital transformation, with a growing need for analysts to manage patient data, improve healthcare outcomes, and optimize operational efficiency.
- E-commerce: E-commerce companies utilize BI and DA to understand customer behavior, personalize marketing campaigns, and optimize supply chain management. Data-driven insights are critical for success in this competitive landscape.
Salary Expectations and Benefits
Salary expectations and benefits packages for BI and DA professionals vary significantly based on experience, location, and specific role. Entry-level positions typically offer competitive starting salaries, coupled with benefits such as health insurance, paid time off, and professional development opportunities. Experienced professionals command significantly higher salaries and often receive more comprehensive benefits packages, including bonuses, stock options, and flexible work arrangements.
For example, a senior data scientist with 10+ years of experience can expect a substantially higher compensation package than a junior analyst just starting their career.
Average Salaries for BI/DA Roles
The following table presents average salary estimates for different BI/DA roles across three major geographical locations. These figures are based on industry reports and online salary databases, and may vary depending on specific company, experience, and skills. Note that these are averages and individual salaries can fluctuate significantly.
| Role | US (USD) | UK (GBP) | India (INR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Analyst | 65,000 – 90,000 | 40,000 – 60,000 | 400,000 – 800,000 |
| Business Intelligence Analyst | 75,000 – 110,000 | 45,000 – 70,000 | 500,000 – 1,000,000 |
| Data Scientist | 100,000 – 150,000+ | 60,000 – 90,000+ | 800,000 – 1,500,000+ |
| Data Engineer | 90,000 – 130,000 | 55,000 – 80,000 | 600,000 – 1,200,000 |
Required Skills and Qualifications: Business Intelligence And Data Analytics Career Opportunities

Landing a dream job in Business Intelligence and Data Analytics requires a potent blend of technical prowess and interpersonal finesse. The field demands professionals who can not only wrangle data but also communicate insights effectively and collaborate seamlessly within a team. This section delves into the specific skills and qualifications needed to thrive in this exciting and rapidly evolving career path.
Success in BI and DA hinges on a combination of hard and soft skills. Technical skills equip you to handle the data, while soft skills ensure you can effectively leverage your findings to drive business decisions. Furthermore, a solid educational foundation provides the necessary theoretical knowledge and practical experience to launch a successful career.
Essential Technical Skills
Proficiency in various technical tools and programming languages is crucial for data manipulation, analysis, and visualization. These skills allow you to extract meaningful insights from raw data and present them in a clear and compelling manner. Mastering these tools is fundamental to your success as a BI and DA professional.
- SQL: Structured Query Language is the backbone of database management. It’s used to extract, manipulate, and manage data within relational databases, a skill highly sought after by employers.
- Python: A versatile programming language widely used for data analysis, machine learning, and automation tasks within BI and DA workflows. Libraries like Pandas and NumPy are essential tools for data manipulation and analysis.
- R: Another powerful programming language specifically designed for statistical computing and graphics. R is particularly useful for advanced statistical modeling and data visualization.
- Tableau: A leading data visualization tool that allows you to create interactive dashboards and reports to effectively communicate complex data insights to stakeholders.
- Power BI: Microsoft’s business analytics service provides a comprehensive suite of tools for data visualization, reporting, and analysis, seamlessly integrating with other Microsoft products.
Essential Soft Skills
While technical skills are essential, strong soft skills are equally important for effective collaboration, communication, and problem-solving within a team environment. These skills ensure that your analytical work translates into actionable business strategies.
- Communication: The ability to clearly and concisely communicate complex data insights to both technical and non-technical audiences is crucial. This includes written reports, presentations, and verbal explanations.
- Problem-solving: BI and DA professionals constantly face challenges in data cleaning, analysis, and interpretation. Strong analytical and problem-solving skills are essential to overcome these obstacles and derive meaningful conclusions.
- Teamwork: Most BI and DA projects are collaborative efforts. Effective teamwork and collaboration skills are crucial for successful project completion and knowledge sharing.
- Critical Thinking: The ability to analyze data objectively, identify biases, and draw accurate conclusions is paramount for effective decision-making based on data-driven insights.
- Business Acumen: Understanding business contexts and how data insights can contribute to strategic decision-making is essential for aligning analytical efforts with business goals.
Educational Pathways
Several educational paths can lead to a successful career in BI and DA. Aspiring professionals can choose from various degree programs, certifications, and online courses, each offering a unique approach to learning and skill development. The best pathway depends on your existing skills and career goals.
- Bachelor’s Degrees: A bachelor’s degree in computer science, statistics, mathematics, or business analytics provides a strong foundation in the theoretical and practical aspects of data analysis.
- Master’s Degrees: A master’s degree in data science, business analytics, or a related field can offer more specialized knowledge and advanced skills, often leading to higher-level positions.
- Certifications: Industry certifications, such as those offered by Google, Microsoft, or AWS, demonstrate proficiency in specific tools and technologies, enhancing your resume and career prospects.
- Online Courses: Numerous online platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udacity offer courses on various aspects of BI and DA, providing flexible and accessible learning opportunities.
Career Paths and Progression
The Business Intelligence and Data Analytics (BI/DA) field offers a diverse range of career paths, each with its own unique trajectory and potential for growth. Understanding these paths and how to navigate them is crucial for anyone aiming for a successful career in this dynamic industry. Progression often involves accumulating experience, developing specialized skills, and taking on increasing responsibilities.
Expand your understanding about powerful RMM software offering comprehensive network monitoring tools with the sources we offer.
The BI/DA field isn’t a monolithic structure; it’s a vibrant ecosystem of interconnected roles. Career advancement is rarely a straight line; it’s more of a journey with various branching paths, depending on individual skills, interests, and opportunities. This section will Artikel some common career paths, illustrating typical progressions and strategies for advancement.
Data Analyst Career Path
Data analysts are the foundation of many BI/DA teams. They collect, clean, and analyze data to identify trends and insights. A typical career progression might start as a Junior Data Analyst, focusing on data cleaning and basic analysis. With experience, they can become a Senior Data Analyst, leading projects, mentoring junior colleagues, and developing more complex analytical models.
Further advancement could lead to a role as a Lead Data Analyst, overseeing multiple projects and teams, or transitioning into a Data Scientist role with a focus on advanced modeling and machine learning.
Data Scientist Career Path
Data scientists are highly skilled professionals who build predictive models and algorithms to solve complex business problems. A common entry point is as a Junior Data Scientist, focusing on applying existing models and techniques. With experience and advanced skills in machine learning and statistical modeling, they can progress to Senior Data Scientist, leading research initiatives and developing innovative solutions.
Further advancement could lead to a Principal Data Scientist, leading a team of data scientists and guiding the overall data science strategy of an organization, or even a Chief Data Scientist role, overseeing all data science efforts within a company.
Business Intelligence Analyst Career Path
Business Intelligence (BI) Analysts focus on translating data insights into actionable business strategies. A typical progression starts as a Junior BI Analyst, learning to use BI tools and create reports. As they gain experience, they can become a Senior BI Analyst, developing more complex dashboards and presentations, and collaborating closely with business stakeholders. Further advancement could lead to a BI Manager, overseeing a team of analysts and the development of the organization’s BI strategy, or even a Director of Business Intelligence, responsible for the overall direction and success of the BI function.
Data Engineer Career Path
Data engineers build and maintain the infrastructure that supports data analysis and machine learning. Starting as a Junior Data Engineer, they focus on data pipelines and database management. With experience, they can become a Senior Data Engineer, designing and implementing complex data architectures. Further advancement might lead to a Lead Data Engineer, overseeing a team of engineers and the development of the organization’s data infrastructure, or even a Chief Data Engineer, responsible for the overall architecture and performance of the organization’s data systems.
Career Progression Strategies
Advancement in BI/DA requires a combination of technical skills, soft skills, and strategic career planning. Continuous learning is essential; staying updated on the latest technologies and analytical techniques is crucial for maintaining competitiveness. Networking with colleagues and industry professionals can open doors to new opportunities and collaborations. Furthermore, gaining project management experience, demonstrating leadership abilities, and effectively communicating complex information to both technical and non-technical audiences are vital for career progression.
Illustrative Career Path Flowchart
Imagine a flowchart. At the bottom, we have “Entry-Level Positions” branching into “Junior Data Analyst,” “Junior Data Scientist,” “Junior BI Analyst,” and “Junior Data Engineer.” Each of these roles then has upward arrows leading to “Senior” versions of the same roles. From the “Senior” level, additional paths emerge. Senior Data Analysts and Senior Data Scientists could progress to “Lead” roles or transition to the other specializations.
Senior BI Analysts could become BI Managers or Directors. Senior Data Engineers could become Lead Data Engineers or Chief Data Engineers. The top of the flowchart would show the most senior roles like Chief Data Scientist, Chief Data Engineer, Director of Business Intelligence, and other high-level leadership positions. The flowchart visually represents the multiple pathways and opportunities for growth within the BI/DA field, emphasizing that progression is not always linear but often involves lateral moves and specialization.
Industry Trends and Future Outlook
The Business Intelligence and Data Analytics (BI&DA) field is experiencing a period of rapid transformation, driven by technological advancements and evolving business needs. Understanding these trends is crucial for professionals seeking to thrive in this dynamic landscape. The convergence of several powerful technologies is reshaping the roles and responsibilities of BI&DA professionals, demanding adaptability and continuous learning.The integration of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and big data technologies is fundamentally altering the way businesses collect, analyze, and utilize data.
This shift necessitates a new set of skills and competencies for professionals to effectively leverage these tools and interpret the insights they generate. The automation potential of these technologies also presents both opportunities and challenges to the job market.
Emerging Technologies Impacting BI and DA
The rise of AI, ML, and big data is revolutionizing the BI&DA landscape. AI-powered tools are automating previously manual tasks, such as data cleaning and report generation, freeing up analysts to focus on higher-level strategic insights. Machine learning algorithms are enabling more sophisticated predictive modeling and anomaly detection, leading to more proactive and data-driven decision-making. Big data technologies, like Hadoop and Spark, allow businesses to process and analyze massive datasets that were previously unmanageable, unlocking new levels of understanding and opportunity.
For example, Netflix uses ML algorithms to personalize recommendations, leading to increased user engagement and retention. Similarly, financial institutions utilize AI to detect fraudulent transactions in real-time, minimizing financial losses.
Future Skills and Competencies in High Demand
In the next 5-10 years, the demand for professionals with a blend of technical and soft skills will continue to increase. Technical skills will include proficiency in programming languages like Python and R, expertise in cloud computing platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP), and experience with various data visualization tools (Tableau, Power BI). Beyond technical skills, strong communication, critical thinking, and problem-solving abilities will be paramount.
The ability to translate complex data insights into actionable recommendations for non-technical stakeholders is increasingly valued. Furthermore, skills in data ethics and privacy will become increasingly critical as businesses navigate complex regulatory landscapes.
Automation and AI’s Reshaping of the BI and DA Job Market
Automation and AI are poised to significantly reshape the BI&DA job market. While some routine tasks will be automated, this will free up analysts to focus on more strategic and creative work. The demand for professionals skilled in designing, implementing, and managing AI-powered BI&DA systems will grow significantly. However, this also means that professionals who lack the adaptability to learn new skills and embrace technological advancements may find their roles becoming obsolete.
The focus will shift from simply analyzing data to interpreting the insights generated by AI and ML models and making strategic recommendations based on those insights. For instance, roles focusing solely on data entry or basic report creation are likely to be automated, while roles requiring advanced analytical skills and strategic thinking will continue to thrive.
Challenges and Opportunities for BI and DA Professionals
The future holds both challenges and opportunities for BI&DA professionals.
- Challenge: Keeping pace with rapid technological advancements and acquiring new skills.
- Opportunity: High demand for skilled professionals, leading to competitive salaries and career growth.
- Challenge: Addressing ethical concerns related to data privacy and bias in algorithms.
- Opportunity: Leading the development and implementation of ethical and responsible AI solutions.
- Challenge: Dealing with the increasing complexity of data and the need for advanced analytical skills.
- Opportunity: Specializing in niche areas like AI-driven predictive modeling or advanced data visualization.
Job Search Strategies and Networking

Landing your dream job in Business Intelligence and Data Analytics requires a strategic approach that goes beyond simply submitting your resume. Success hinges on a proactive job search, effective networking, and a compelling presentation of your skills and experience. This section Artikels key strategies to maximize your chances of securing a rewarding career in this dynamic field.
The BI and DA job market is competitive, demanding a well-defined strategy encompassing online and offline avenues. A multi-pronged approach significantly increases your visibility and opportunities.
Effective Job Search Methods
Utilizing a variety of platforms is crucial for maximizing your reach. Don’t rely on a single source; instead, diversify your search to uncover hidden opportunities.
- Online Job Boards: Sites like LinkedIn, Indeed, Glassdoor, and specialized data science job boards offer a vast pool of openings. Regularly search using relevant s like “Business Intelligence Analyst,” “Data Scientist,” “Data Analyst,” and “Data Engineer,” tailoring your search to specific industries or technologies you’re interested in.
- Company Websites: Many companies post job openings directly on their career pages. This allows you to target specific organizations you admire and learn more about their culture before applying.
- Networking Events: Attend industry conferences, meetups, and workshops to connect with professionals in the field. These events offer opportunities to learn about new trends, build relationships, and discover unadvertised job openings.
- Recruiters: Connect with recruiters specializing in BI and DA roles. They often have access to unadvertised positions and can provide valuable insights into the job market.
Crafting a Compelling Resume and Cover Letter
Your resume and cover letter are your first impression; make them count. Tailor each application to the specific job description, highlighting relevant skills and experiences.
- Resume: Use a clean and professional format, emphasizing quantifiable achievements and results. Use s from the job description to improve your chances of Applicant Tracking System (ATS) detection. Showcase projects demonstrating your proficiency in tools like SQL, Python, Tableau, or Power BI.
- Cover Letter: Personalize each cover letter to reflect your understanding of the company and the specific role. Clearly articulate your skills and experience relevant to the job requirements and explain why you’re a strong fit for the company’s culture.
Interview Preparation
Thorough preparation is essential for success in BI and DA interviews. Expect a mix of behavioral questions and technical assessments designed to evaluate your skills and problem-solving abilities.
- Behavioral Questions: Practice answering common behavioral interview questions using the STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result). Prepare examples that demonstrate your teamwork, communication, problem-solving, and analytical skills.
- Technical Assessments: Prepare for technical questions related to SQL, data visualization, statistical analysis, and machine learning algorithms. Practice coding challenges and prepare to explain your approach to problem-solving. Review your projects and be prepared to discuss your contributions and the technologies you used.
Building a Professional Network
Networking is vital for long-term career success in BI and DA. Actively cultivate relationships with professionals in the field to gain insights, learn about new opportunities, and receive mentorship.
- Conferences and Meetups: Attend industry events to meet professionals, learn about new trends, and expand your network. Actively participate in discussions and exchange contact information.
- Online Forums and Communities: Engage in online forums and communities dedicated to BI and DA, such as Stack Overflow or LinkedIn groups. Share your knowledge, ask questions, and participate in discussions to build your reputation and connect with others.
- Mentorship: Seek out mentors who can provide guidance and support. A mentor can offer valuable advice on career paths, job search strategies, and industry trends.