Future trends and innovations in remote monitoring and management (RMM) software are reshaping how businesses manage their IT infrastructure. From the rise of AI-powered predictive maintenance to enhanced remote access capabilities and robust cybersecurity features, RMM is undergoing a significant transformation. This evolution is driven by the increasing complexity of IT environments, the growth of remote work, and the ever-present threat of cyberattacks.
We’ll dive into the key advancements shaping the future of RMM, exploring how these innovations are impacting efficiency, security, and overall IT management.
This exploration will cover the shift towards cloud-based architectures, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for proactive issue resolution, and the crucial enhancements in cybersecurity measures. We’ll also look at how RMM is adapting to the challenges and opportunities presented by the Internet of Things (IoT) and the evolving landscape of remote work. Get ready to discover how RMM is not just keeping up with technological advancements, but actively shaping them.
Evolving RMM Software Architectures
The landscape of Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) software is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the increasing demand for scalability, flexibility, and enhanced security. This evolution is primarily characterized by a shift away from traditional, on-premises client-server models towards cloud-based and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) architectures. This change offers significant advantages in terms of accessibility, cost-effectiveness, and ease of management.The shift to cloud-based RMM represents a paradigm shift in how businesses manage their IT infrastructure.
Cloud-based solutions leverage the power of remote servers and data centers, eliminating the need for on-site hardware and infrastructure maintenance. This results in reduced capital expenditure, simplified updates and patching, and improved accessibility for IT administrators, regardless of their physical location. This accessibility is particularly crucial in today’s increasingly distributed workforce.
Client-Server to Cloud-Based and SaaS Architectures
Traditional client-server RMM models relied on dedicated servers within a company’s infrastructure. These systems required significant upfront investment in hardware, software licenses, and dedicated IT personnel for maintenance and updates. In contrast, cloud-based and SaaS RMM solutions leverage the scalability and reliability of cloud infrastructure providers like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. This eliminates the need for on-site hardware, reducing capital expenditures and operational overhead.
Furthermore, SaaS models typically offer subscription-based pricing, making them more cost-effective for smaller businesses. Companies like Datto, ConnectWise, and Kaseya are prime examples of providers successfully navigating this transition, offering robust cloud-based RMM solutions that cater to diverse business needs. The move to the cloud allows for automated patching, improved scalability to handle fluctuating workloads, and easier collaboration among IT teams.
Security Implications of On-Premise vs. Cloud-Based RMM
The security implications of choosing between on-premises and cloud-based RMM solutions are significant and require careful consideration. While both offer security features, their implementation and management differ considerably.
| Security Feature | On-Premise | Cloud-Based | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Security | Responsibility lies solely with the organization. Requires robust internal security measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits. | Shared responsibility model; the cloud provider manages the underlying infrastructure security, while the organization is responsible for data and application security. Leverages cloud provider’s security expertise and infrastructure. | Cloud-based solutions benefit from the security expertise and robust infrastructure of the provider, but organizations still need to implement appropriate data protection measures. |
| Access Control | Managed internally through user accounts and permissions. Requires careful management to prevent unauthorized access. | Typically utilizes multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, and other advanced security features provided by the cloud provider. | Cloud-based solutions often offer more granular and sophisticated access control mechanisms, enhancing security. |
| Disaster Recovery | Requires significant planning and investment in backup and recovery infrastructure. Downtime can be extensive in case of a disaster. | Cloud providers typically offer robust disaster recovery capabilities, including data replication and failover mechanisms, minimizing downtime. | Cloud-based solutions offer significantly improved disaster recovery capabilities, reducing the risk of data loss and service disruption. |
| Compliance | Organization is solely responsible for ensuring compliance with relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). | Cloud providers often offer compliance certifications (e.g., ISO 27001, SOC 2) that can help organizations meet regulatory requirements. | Cloud-based solutions can simplify compliance efforts by leveraging the provider’s existing certifications and security measures. |
The Role of APIs and Integrations in Modern RMM Systems
Modern RMM systems are increasingly reliant on Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and seamless integrations to enhance functionality and streamline workflows. APIs allow RMM platforms to connect with other software solutions, creating a unified and efficient IT management ecosystem. For example, integration with ticketing systems (e.g., ServiceNow, Jira) enables automated ticket creation and updates based on RMM alerts. Integration with PSA (Professional Services Automation) tools allows for streamlined billing and project management.
Furthermore, integrations with monitoring tools (e.g., network monitoring, security information and event management (SIEM) systems) provide a comprehensive view of the IT infrastructure, enabling proactive issue resolution. The ability to integrate with a wide range of third-party applications is a key differentiator for modern RMM platforms, enabling businesses to customize their IT management solutions to meet specific needs.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in RMM: Future Trends And Innovations In Remote Monitoring And Management (RMM) Software
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) is revolutionizing Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) software, transforming it from a reactive tool to a proactive, predictive powerhouse. This shift allows IT teams to move beyond simply addressing existing issues to anticipating and preventing problems before they impact end-users, significantly improving efficiency and reducing downtime. The core functionalities of RMM are being enhanced by these technologies, leading to more streamlined workflows and enhanced security.AI and ML are not merely supplementary features; they are fundamentally reshaping the architecture and capabilities of modern RMM platforms.
This allows for more sophisticated analysis of vast datasets, enabling quicker identification of anomalies, and ultimately, more effective problem resolution. The result is a more efficient, secure, and cost-effective IT management experience.
Predictive Maintenance and Proactive Issue Resolution using AI
AI algorithms analyze historical data, such as system logs, performance metrics, and hardware sensor readings, to identify patterns indicative of impending failures. For example, an AI-powered RMM system might detect a gradual increase in hard drive read/write errors on a specific server, predicting a potential hard drive failure within the next few weeks. This allows IT administrators to proactively replace the failing component before it causes a system crash or data loss, minimizing disruption and avoiding costly emergency repairs.
This predictive capability extends beyond hardware; AI can also predict software vulnerabilities and potential performance bottlenecks based on usage patterns and system configurations. Imagine a scenario where an AI system flags a potential overload on a network segment before it impacts user experience, allowing for proactive capacity upgrades.
Improved Threat Detection and Response with ML Algorithms
Machine learning algorithms excel at identifying subtle patterns and anomalies that might escape human detection. In the context of RMM, ML algorithms can analyze network traffic, system events, and security logs to identify malicious activities such as malware infections, unauthorized access attempts, and data breaches. These algorithms continuously learn and adapt, improving their accuracy over time as they process more data.
For instance, an ML model trained on a large dataset of known malware signatures and attack patterns can detect new, previously unseen threats with high accuracy. This proactive approach significantly enhances the security posture of managed systems and reduces the risk of costly security breaches. Furthermore, the integration of ML-powered threat intelligence feeds enables the RMM system to proactively patch vulnerabilities and apply security updates before attackers can exploit them.
AI-Powered Automation Streamlining RMM Workflows
Consider a scenario where a large enterprise uses an AI-powered RMM system to manage thousands of endpoints. Previously, tasks such as software patching, security updates, and system backups would require significant manual effort and coordination across multiple IT teams. Now, an AI-powered RMM system can automate these tasks, intelligently scheduling them based on factors like system load, network availability, and user activity.
This automation not only saves time and reduces operational costs but also ensures that critical updates and backups are applied consistently across all managed systems. Furthermore, AI can automate incident response, diagnosing and resolving common issues without human intervention. For example, the system might automatically restart a frozen application or reconfigure network settings to resolve a connectivity problem, significantly reducing the workload on IT support staff and improving overall user experience.
This level of automation allows IT teams to focus on more strategic tasks, such as system optimization and long-term planning.
Enhanced Remote Access and Control Capabilities

Remote access and control are the bedrock of any effective RMM solution. While traditional methods like VNC and RDP have served us well, the demand for more secure, efficient, and user-friendly remote access is driving innovation in this space. Next-generation RMM platforms are moving beyond these legacy technologies, incorporating advanced features that streamline troubleshooting and improve the overall user experience for both technicians and end-users.Advancements in remote control technologies significantly boost both user experience and technician efficiency.
Faster connection speeds, improved bandwidth management, and sophisticated session management tools minimize downtime and frustration. Features like session recording, automated scripting, and enhanced security protocols contribute to a more seamless and secure remote support experience. This translates directly into reduced resolution times, lower support costs, and increased customer satisfaction.
Innovative Remote Access Technologies
Beyond VNC and RDP, several innovative technologies are transforming remote access. These include technologies leveraging HTML5 for browser-based access, eliminating the need for dedicated clients and improving cross-platform compatibility. Furthermore, we’re seeing the rise of enhanced SSH capabilities that allow for secure command-line access and remote execution of scripts, perfect for server administration. Finally, the integration of augmented reality (AR) overlays in remote sessions is emerging, allowing technicians to guide users through complex tasks visually, directly on the user’s screen, providing context-sensitive support.
Imagine a technician remotely guiding a user to replace a faulty component by overlaying instructions directly onto the user’s camera view of their device.
Improved User Experience and Technician Efficiency
Modern RMM solutions are emphasizing intuitive interfaces and streamlined workflows. Features like context-aware assistance, which anticipates the technician’s next step based on the current issue, drastically improve efficiency. Integrated chat functionality allows for real-time communication between the technician and the user, fostering collaboration and speeding up resolution. Automated session recording provides valuable training materials and helps to improve the quality of support provided over time.
These features combined lead to significant improvements in first-call resolution rates and overall customer satisfaction.
Get the entire information you require about Future trends in HRIS technology and its impact on HR on this page.
Next-Generation RMM Remote Access Module UI Mockup
Imagine a clean, modern interface with a central pane displaying the remote desktop. On the left, a collapsible sidebar offers quick access to tools: a session recording toggle, a chat window, a script library for automated tasks, and a contextual help menu. The top bar displays session information (connection speed, latency, duration) and allows for quick access to advanced features such as screen sharing, file transfer, and command-line access.
The right sidebar displays system information from the remote machine (CPU usage, memory, disk space) in real-time, providing valuable context for troubleshooting. The overall aesthetic is minimalist and intuitive, focusing on ease of use and efficient workflow. The benefit is a user-friendly interface that reduces the learning curve for technicians and enhances their ability to quickly diagnose and resolve issues, ultimately increasing customer satisfaction and reducing support costs.
Cybersecurity Enhancements in RMM
The rise of remote work and the increasing reliance on interconnected devices have significantly amplified the attack surface for businesses. This makes robust cybersecurity within Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) systems absolutely critical, not just a nice-to-have. Modern RMM platforms are evolving to address these escalating threats, integrating advanced security features to protect both the RMM infrastructure itself and the managed endpoints.
Let’s delve into the crucial cybersecurity advancements shaping the future of RMM.RMM systems are increasingly becoming prime targets for sophisticated cyberattacks. These attacks leverage vulnerabilities in the RMM software itself or exploit weaknesses in the managed endpoints to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data and disrupt business operations. Emerging threats include supply chain attacks targeting RMM vendors, phishing campaigns aimed at administrators, and lateral movement within networks once initial access is gained.
The consequences can range from data breaches and financial losses to complete operational paralysis.
Advanced Security Features in RMM
Modern RMM solutions are incorporating several advanced security features to mitigate these risks. Multi-factor authentication (MFA), for instance, adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple forms of authentication before granting access to the RMM platform. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access even if credentials are compromised. Behavioral analysis employs machine learning algorithms to identify anomalies in system activity, flagging potentially malicious behavior before it can cause significant damage.
For example, an unusual spike in file access attempts from an unknown location might trigger an alert. Finally, integration with Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions provides real-time threat detection and response capabilities at the endpoint level, enabling faster identification and remediation of security incidents. EDR enhances the RMM’s ability to proactively identify and neutralize malware and other threats.
Vulnerability Management Approaches in RMM
Effective vulnerability management is paramount in maintaining a secure RMM environment. Different approaches exist, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
The following points compare and contrast different vulnerability management approaches within RMM platforms:
- Automated Vulnerability Scanning: This approach uses automated tools to regularly scan endpoints for known vulnerabilities. It’s efficient for identifying common vulnerabilities but might miss zero-day exploits or configuration issues not covered in the vulnerability database.
- Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing: This more comprehensive approach combines automated scanning with manual analysis and penetration testing to identify a wider range of vulnerabilities, including those not easily detected by automated tools. It’s more thorough but also more time-consuming and expensive.
- Patch Management: This involves automatically deploying security patches to endpoints to address known vulnerabilities. It’s crucial for mitigating the impact of known vulnerabilities but requires careful planning and testing to avoid disruptions to operations.
- Configuration Management: This focuses on ensuring that endpoints are configured securely, reducing the attack surface. It complements vulnerability scanning and patch management by addressing configuration-related vulnerabilities that might not be addressed by other methods.
Automation and Orchestration in RMM
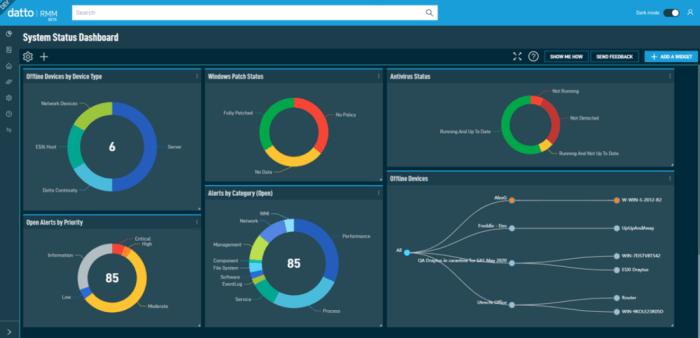
The relentless pace of technological advancement demands equally agile IT management solutions. Manual processes, once commonplace, are now significant bottlenecks in maintaining a robust and secure digital infrastructure. This is where the power of automation and orchestration in Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) software becomes undeniable, transforming how IT teams manage and secure their networks. By automating repetitive tasks and intelligently integrating various IT tools, RMM platforms drastically improve operational efficiency, freeing up valuable time for strategic initiatives.Automation in RMM streamlines routine tasks, significantly reducing manual intervention.
Imagine the time saved by automating patch management, software deployment, or even basic troubleshooting. This isn’t just about convenience; it’s about minimizing human error and ensuring consistent application of best practices across all managed devices. The result is a more reliable, secure, and efficient IT environment. Orchestration, on the other hand, takes this a step further by enabling seamless communication and data exchange between different IT management tools.
This integrated approach eliminates data silos, provides a unified view of the IT landscape, and empowers IT teams to respond to incidents and implement changes with unprecedented speed and precision. For example, an automated workflow could trigger a ticket in a help desk system upon detection of a critical security vulnerability, automatically initiating the patching process and then sending a notification to the affected user.
This coordinated response minimizes downtime and enhances overall security posture.
Automated Patching and Updating Workflow
A well-designed automated patching and updating workflow is critical for maintaining system security and stability. This process leverages the power of RMM to automatically identify outdated software, download the necessary patches, and deploy them to managed devices, all with minimal human intervention. The following flowchart illustrates a typical automated workflow: Imagine a flowchart with four distinct boxes connected by arrows. The first box, labeled “Device Inventory Scan,” shows the RMM system scanning all managed devices to identify their current software versions. An arrow points to the second box, “Patch Identification,” where the RMM system compares the identified versions against a known vulnerability database, identifying devices requiring updates. An arrow leads to the third box, “Automated Patch Deployment,” where the RMM system downloads and installs the necessary patches on the identified devices. Finally, an arrow points to the fourth box, “Verification and Reporting,” where the RMM system verifies the successful installation of the patches and generates a report detailing the process. This automated process ensures that all devices are up-to-date with the latest security patches and software updates, minimizing vulnerabilities and enhancing overall system security.
Benefits of RMM Orchestration with Other IT Management Tools
Integrating RMM with other IT management tools, such as ticketing systems, security information and event management (SIEM) platforms, and network monitoring systems, provides a holistic view of the IT infrastructure. This integrated approach improves incident response times, enhances collaboration among IT teams, and allows for proactive identification and mitigation of potential issues. For example, integrating RMM with a SIEM system can automatically trigger an alert when a security incident is detected, allowing for immediate response and minimizing the impact of the breach.
This integrated approach leads to significant improvements in operational efficiency and reduces the overall cost of IT management. Consider a scenario where a network monitoring tool detects a performance bottleneck. Through orchestration, this information can automatically trigger an investigation within the RMM system, leading to the identification and resolution of the issue without manual intervention. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and ensures optimal system performance.
The Rise of IoT and its Impact on RMM
The explosion of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in both personal and professional settings presents both exciting opportunities and significant challenges for Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) software. Integrating these diverse devices into existing RMM frameworks requires a fundamental shift in approach, demanding solutions capable of handling vastly different device types, communication protocols, and security needs. The sheer volume and heterogeneity of IoT devices necessitate innovative RMM solutions designed for scalability and efficient management.The increasing reliance on IoT devices across various sectors, from smart homes and industrial automation to healthcare and smart cities, significantly expands the attack surface.
This necessitates robust security measures within the RMM framework to mitigate the risks associated with managing a vast network of often-vulnerable devices. The ability to effectively monitor, manage, and secure IoT devices is becoming increasingly critical for organizations seeking to maintain operational efficiency and protect sensitive data.
Challenges and Opportunities Presented by IoT Device Management
The integration of IoT devices into RMM presents a unique set of challenges. The sheer diversity of IoT devices, each with its own operating system, communication protocols, and security features, creates complexity in managing and monitoring them effectively. This heterogeneity requires RMM solutions that are highly adaptable and capable of supporting a wide range of device types. Simultaneously, the proliferation of IoT devices presents immense opportunities for improved operational efficiency, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision-making.
For example, RMM can provide real-time monitoring of industrial equipment, enabling predictive maintenance and minimizing downtime. In healthcare, remote monitoring of patient devices via RMM can lead to improved patient care and reduced hospital readmissions.
Security Considerations for Managing IoT Devices
Security is paramount when managing IoT devices within an RMM framework. Many IoT devices lack robust security features, making them vulnerable to cyberattacks. These vulnerabilities can expose sensitive data and disrupt operations. RMM solutions must incorporate advanced security features such as device authentication, encryption, and vulnerability scanning to mitigate these risks. Regular firmware updates and secure configuration management are also crucial to maintaining the security posture of IoT devices.
A layered security approach, integrating network security measures with device-level security controls, is essential to protecting against sophisticated attacks. Failure to adequately address these security concerns can lead to significant financial and reputational damage. Consider the 2021 Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack, highlighting the vulnerability of critical infrastructure to cyberattacks targeting IoT devices.
RMM Features Designed for IoT Device Management
The effective management of IoT devices requires specialized RMM features. Below is a table outlining key features, their descriptions, and the benefits they provide:
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Device Discovery and Inventory | Automatically identifies and catalogs all IoT devices connected to the network, providing a comprehensive inventory of connected devices. | Improved visibility into the network, enabling proactive management and security assessments. |
| Remote Firmware Updates | Distributes and installs firmware updates to IoT devices remotely, ensuring devices are running the latest, most secure versions of their software. | Enhanced security posture and reduced vulnerability to exploits. |
| Customizable Dashboards and Reporting | Provides customizable dashboards that display real-time data and generate reports on the performance and health of IoT devices. | Improved monitoring and proactive identification of potential problems. |
| Security Auditing and Compliance | Tracks device activity and configurations, ensuring compliance with security policies and regulations. | Reduced risk of security breaches and improved regulatory compliance. |
RMM and the Future of Work
The dramatic shift towards remote and hybrid work models has fundamentally reshaped the IT landscape. Businesses now rely heavily on technology to maintain productivity and security, making robust Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) solutions not just a luxury, but a critical necessity. The increasing reliance on dispersed workforces has amplified the demand for sophisticated RMM capabilities, driving innovation and shaping the future of work itself.The impact of remote work trends on the demand for robust RMM solutions is undeniable.
With employees accessing company resources from diverse locations and devices, centralized management and security become paramount. Traditional on-site IT support is no longer sufficient; instead, businesses need solutions that offer real-time monitoring, proactive problem-solving, and secure remote access, all essential components of effective RMM software. This shift has fueled the development of more sophisticated and user-friendly RMM platforms capable of handling the complexities of a geographically dispersed workforce.
Companies like Zoom, Slack, and Microsoft Teams have seen explosive growth, highlighting the increasing reliance on digital collaboration tools, a trend directly supported by the capabilities of modern RMM systems.
RMM’s Role in Facilitating Collaboration Among Geographically Dispersed IT Teams
Effective communication and collaboration are crucial for maintaining a productive and secure remote workforce. RMM software plays a vital role by providing a centralized platform for IT teams to manage and monitor all connected devices and systems, regardless of location. This centralized view allows for streamlined troubleshooting, quicker response times to issues, and efficient deployment of updates and patches.
Features such as shared dashboards, integrated communication tools, and automated reporting foster seamless collaboration among IT professionals, regardless of their physical location. For instance, an IT team in New York can remotely troubleshoot a server issue in London using RMM’s remote access and control capabilities, demonstrating the software’s power in bridging geographical divides.
Key RMM Features Supporting a Fully Remote Workforce, Future trends and innovations in remote monitoring and management (RMM) software
The effectiveness of a fully remote workforce hinges on the capabilities of the RMM software employed. A robust RMM solution needs several key features to ensure smooth operations and enhanced security.
- Comprehensive Device Management: Ability to monitor and manage all endpoints (laptops, desktops, mobile devices, servers) from a single pane of glass, irrespective of location or operating system.
- Advanced Security Features: Integrated security tools such as endpoint detection and response (EDR), vulnerability scanning, and patch management are crucial for safeguarding company data and systems from cyber threats.
- Secure Remote Access and Control: Robust and secure methods for remotely accessing and controlling endpoints, allowing IT teams to quickly troubleshoot and resolve issues without physical presence.
- Automated Patch Management: Automated deployment of software updates and security patches to all endpoints, minimizing vulnerabilities and ensuring compliance.
- Real-time Monitoring and Alerting: Proactive monitoring of system performance and security, with immediate alerts on potential issues, allowing for prompt intervention and prevention of downtime.
- Integrated Ticketing and Help Desk System: Streamlined process for managing and tracking IT support requests, ensuring efficient resolution of user issues.
- Reporting and Analytics: Detailed reporting and analytics to track system performance, security incidents, and IT support efficiency.