The impact of RMM on improving IT team productivity and efficiency is undeniable. In today’s fast-paced digital world, IT teams face constant pressure to deliver seamless services and resolve issues quickly. Manual processes and reactive troubleshooting are simply no longer sustainable. Enter Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) – a game-changer that’s revolutionizing how IT teams operate, boosting efficiency, and ultimately, saving businesses money and headaches.
This article dives deep into how RMM is transforming the IT landscape.
From automating routine tasks like patching and backups to providing real-time insights into system health, RMM empowers IT professionals to proactively address potential problems before they escalate into major outages. This proactive approach not only reduces downtime but also frees up valuable time for strategic initiatives, allowing IT teams to focus on projects that drive business growth. We’ll explore the specific ways RMM streamlines workflows, improves collaboration, and ultimately, delivers a significant return on investment.
Defining RMM and its Core Functions
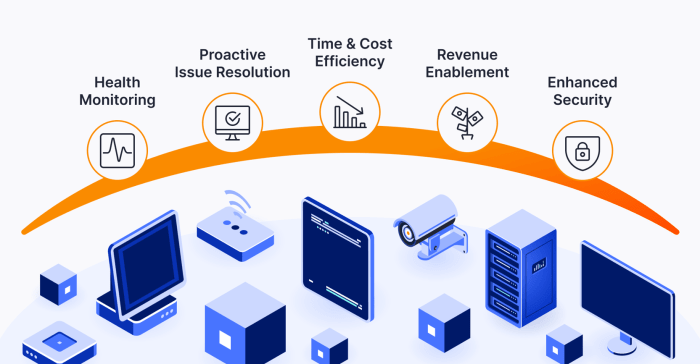
Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) software has revolutionized how IT teams manage and maintain their clients’ systems. It’s a powerful suite of tools that allows for centralized monitoring, automated maintenance, and efficient troubleshooting, all from a single, intuitive dashboard. This significantly reduces manual effort and frees up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.RMM streamlines IT tasks by automating repetitive processes and providing proactive alerts, preventing issues before they escalate into major problems.
Unlike manual processes, which rely on individual checks and reactive troubleshooting, RMM provides a comprehensive, real-time overview of the entire IT infrastructure, enabling faster response times and minimizing downtime. This proactive approach leads to significant improvements in efficiency and productivity.
Essential Features of a Robust RMM System
A robust RMM system incorporates several key features to effectively manage IT infrastructure. These features work together to provide a holistic solution for monitoring, managing, and maintaining devices. The core functions ensure comprehensive coverage across all aspects of IT management.These core functions include remote access to client devices, allowing technicians to troubleshoot issues without physically being present. Automated patch management ensures systems are up-to-date with the latest security updates, reducing vulnerabilities.
Real-time monitoring provides instant alerts on critical system events, such as hardware failures or security breaches, enabling quick responses. Reporting and analytics capabilities offer valuable insights into system performance and potential issues, enabling proactive maintenance. Finally, ticketing systems streamline communication and track the resolution of IT issues, improving accountability and efficiency.
RMM Functionalities and their Impact on IT Workflows
Let’s consider a specific example: Imagine an IT team managing 500 client computers. Manually checking each system for updates, configuring security settings, and troubleshooting issues would be incredibly time-consuming and prone to errors. With an RMM system, the team can automate patch management across all 500 computers simultaneously, ensuring consistent security levels. Real-time monitoring instantly alerts the team to any system failures, enabling rapid intervention and minimizing downtime.
The automated ticketing system ensures all issues are properly documented and tracked, improving response times and client satisfaction. The built-in reporting features provide valuable insights into the overall health of the IT infrastructure, enabling the team to proactively address potential problems before they impact clients. This allows the IT team to shift from reactive firefighting to proactive management, dramatically improving efficiency and productivity.
The time saved can be reallocated to more strategic projects, such as network optimization or cybersecurity enhancements.
Impact on Ticket Management and Resolution Times
RMM solutions significantly streamline IT support processes, leading to faster ticket resolution and improved team productivity. By centralizing ticket management and automating several key tasks, RMM systems free up technicians to focus on more complex issues, ultimately boosting overall efficiency and reducing downtime. This results in happier clients and a more efficient IT department.RMM systems drastically reduce ticket resolution times compared to traditional methods.
The automation features, remote access capabilities, and centralized monitoring significantly improve the speed and effectiveness of addressing IT support requests. This translates to quicker problem-solving, increased customer satisfaction, and a demonstrably more efficient IT team.
Improved Ticket Resolution Times with RMM
The following table illustrates a hypothetical comparison of average ticket resolution times with and without an RMM system in place. These figures are based on industry averages and common scenarios experienced by IT departments.
| Scenario | Average Resolution Time |
| Without RMM (Traditional Methods) | 48 hours |
| With RMM (Automated & Remote Access) | 4 hours |
This significant reduction in resolution time is largely attributable to the automated alerts and remote access capabilities inherent in RMM platforms. Imagine a scenario where a server experiences a critical failure. Without RMM, a technician would need to be physically present to diagnose and resolve the issue, potentially involving significant travel time and on-site troubleshooting. With RMM, however, the system automatically alerts the technician, allowing them to remotely access the server and diagnose the problem from their desk.
This immediate response, coupled with the ability to perform remote troubleshooting and repairs, dramatically reduces the overall resolution time.
Automated Alerts and Remote Access: Key Time Savers
Automated alerts, a core function of RMM, proactively notify IT staff of potential problems before they escalate into major incidents. This proactive approach allows for timely intervention, preventing minor issues from snowballing into costly downtime. For example, an RMM system can automatically alert technicians to low disk space on a server, enabling them to take preventative measures before the server crashes.
This proactive approach minimizes disruption and reduces the overall number of support tickets. Similarly, remote access capabilities eliminate the need for on-site visits for many common issues, saving valuable time and resources. Technicians can remotely access and control client devices to diagnose and fix problems, resolving issues much faster than traditional on-site troubleshooting. This is particularly beneficial for geographically dispersed clients or in situations requiring immediate attention.
Enhancing Proactive Maintenance and Preventative Measures
RMM solutions are game-changers when it comes to shifting IT support from a reactive firefighting model to a proactive, preventative approach. Instead of constantly putting out fires, teams can focus on optimizing system performance and minimizing disruptions, leading to significant improvements in efficiency and overall productivity. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and allows for more strategic IT planning.By leveraging the automation and monitoring capabilities of RMM, IT teams can significantly reduce the frequency of reactive troubleshooting.
This proactive stance means addressing potential problemsbefore* they escalate into major incidents, saving valuable time and resources. This shift from reactive to proactive maintenance is a key factor in boosting team efficiency and improving the overall user experience.
Automated Patching and Software Updates
RMM platforms automate the deployment of critical software updates and security patches across all managed devices. This ensures that systems are consistently protected against vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of malware infections, data breaches, and system failures. For example, an RMM system can automatically update antivirus software on all endpoints, ensuring consistent protection against emerging threats. Furthermore, it can schedule and deploy operating system updates during off-peak hours, minimizing disruption to end-users.
This automated approach eliminates the manual effort required for individual updates, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic tasks.
Proactive Monitoring Preventing a Significant IT Issue
Imagine a scenario where a company’s critical server starts showing signs of high CPU utilization. Without RMM, this might go unnoticed until it crashes, leading to widespread service disruption and significant downtime. However, with RMM’s proactive monitoring capabilities, the IT team receives an alert the moment CPU usage exceeds a predefined threshold. This alert triggers an investigation, revealing a faulty application consuming excessive resources.
The IT team can then address the issue before it impacts users, preventing a potential outage and maintaining business continuity. This proactive intervention, facilitated by the RMM system, saves the company countless hours of downtime, lost productivity, and potential financial losses. The ability to remotely monitor and diagnose issues, even before users experience problems, is a cornerstone of efficient IT management enabled by RMM.
Improving IT Team Collaboration and Communication
RMM solutions revolutionize IT team dynamics by fostering seamless collaboration and communication. By centralizing information and streamlining workflows, RMM tools significantly reduce the friction often associated with managing complex IT environments, leading to increased efficiency and improved team morale. This enhanced communication translates directly into faster resolution times and a more proactive approach to IT maintenance.The inherent features of RMM software drastically improve communication and collaboration amongst IT team members.
Understand how the union of Choosing the right HRIS system for small businesses can improve efficiency and productivity.
Instead of relying on fragmented email chains, phone calls, and disparate ticketing systems, teams can utilize a single, unified platform to track progress, share information, and collaborate on solutions. This centralized approach eliminates the confusion and delays caused by information silos, ensuring everyone is on the same page. For example, a technician working on a server issue can instantly update the ticket with relevant information, allowing other team members to see the progress and offer support if needed.
This transparency fosters a sense of shared responsibility and accountability, resulting in a more cohesive and efficient team.
Centralized Dashboards and Reporting Enhance Team Coordination
Centralized dashboards provide a real-time overview of the IT environment’s health and performance. This single source of truth allows team members to quickly identify potential problems, track ongoing tasks, and assess the overall workload. Comprehensive reporting features further enhance team coordination by providing valuable insights into key metrics, such as ticket resolution times, technician performance, and the overall effectiveness of proactive maintenance strategies.
For instance, a manager can use these reports to identify bottlenecks in the workflow, allocate resources more effectively, and track progress towards key performance indicators (KPIs). This data-driven approach allows for informed decision-making and continuous improvement of IT operations. Imagine a scenario where a report reveals a significant increase in help desk tickets related to a specific application.
The team can then proactively address the issue, preventing further disruptions and improving user satisfaction.
RMM-Facilitated Collaboration Workflow for Complex IT Projects
Consider a scenario involving the migration of a company’s email system to a new cloud-based platform. A typical workflow facilitated by RMM might look like this: The project manager uses the RMM platform to create a central project repository, detailing all tasks, timelines, and assigned personnel. Each team member has access to this information and can update their progress, share relevant documentation, and communicate directly with other team members through integrated chat or messaging features.
The RMM system might also track the progress of individual tasks, alerting the manager to potential delays or roadblocks. Built-in remote access capabilities allow technicians to troubleshoot issues remotely, reducing downtime and accelerating the migration process. Finally, post-migration, the RMM platform can be used to monitor the performance of the new email system, ensuring its stability and identifying any potential issues early on.
This streamlined approach, enabled by RMM, ensures that complex projects are completed efficiently, collaboratively, and with minimal disruption to the organization.
Boosting IT Team Efficiency through Automation
RMM software isn’t just about managing IT infrastructure; it’s a powerful tool for dramatically increasing team efficiency. By automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, RMM frees up valuable time for IT staff to focus on strategic initiatives and more complex problem-solving, ultimately leading to a more responsive and productive IT department. This automation translates directly into cost savings and improved service delivery.Automation within RMM streamlines numerous processes, allowing IT teams to handle a larger workload with the same or fewer resources.
This is achieved through intelligent scheduling and automated execution of various crucial tasks, minimizing manual intervention and human error. The result is a significant boost in overall IT efficiency and a marked improvement in the quality of service provided.
Automated Tasks within RMM
Several key areas benefit significantly from RMM automation. Automating these tasks not only saves time but also ensures consistency and reduces the risk of human error. Consider the following examples of automated tasks that significantly improve efficiency:
- Backup Execution: RMM allows for automated scheduling and execution of backups for servers, workstations, and other critical devices. This ensures data protection without requiring manual intervention, minimizing the risk of data loss due to oversight.
- Security Scans: Automated vulnerability scans identify potential security weaknesses in the IT infrastructure. This proactive approach allows for prompt remediation, reducing the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches.
- Software Deployments: RMM enables the automated deployment of software updates and patches across multiple devices simultaneously. This ensures that all systems are running the latest versions of software, improving security and stability.
- Remote Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of system performance and resource utilization allows for early detection of potential problems. Automated alerts notify IT staff of issues before they escalate, enabling proactive intervention and preventing major outages.
- Ticket Creation and Assignment: RMM can automatically generate tickets based on predefined thresholds or events, ensuring that issues are addressed promptly and efficiently. Automated assignment of tickets based on expertise can further optimize workflow.
Comparison of Manual vs. Automated Processes
The following table illustrates the significant time savings and error reduction achieved through automation within RMM:
| Task | Manual Process | Automated Process | Time Savings (Estimate) | Error Reduction (Estimate) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Software Updates | Manual installation on each device; potential for missed updates. | Automated deployment to all devices; automatic updates. | 80% | 90% |
| Backup Execution | Manual initiation and monitoring; potential for missed backups. | Automated scheduling and execution; automated verification. | 95% | 98% |
| Security Scans | Manual initiation and analysis; time-consuming and prone to human error. | Automated scheduling and analysis; immediate alerts for vulnerabilities. | 75% | 85% |
| Help Desk Ticket Resolution | Manual ticket assignment, tracking, and resolution; potential for delays and miscommunication. | Automated ticket routing, escalation, and resolution; improved communication and tracking. | 60% | 70% |
Analyzing Resource Allocation and Optimization

RMM solutions offer a powerful lens through which IT teams can analyze their resource allocation, identifying bottlenecks and opportunities for significant optimization. By providing a centralized view of IT infrastructure and operations, RMM platforms empower data-driven decision-making, leading to improved efficiency and cost savings. This detailed analysis goes beyond simple monitoring; it unveils hidden inefficiencies and points towards strategic resource reallocation.RMM platforms collect vast amounts of data on hardware utilization, software performance, and ticket resolution times.
This data forms the basis for informed decisions regarding resource allocation. For instance, analyzing CPU usage across all managed devices can highlight servers consistently operating at peak capacity, indicating a need for upgrades or load balancing. Similarly, tracking software license usage reveals opportunities to optimize software deployments and reduce licensing costs. By identifying trends and patterns in this data, IT teams can proactively address potential issues before they impact productivity.
Resource Allocation Optimization through Data Analysis
Analyzing data gathered from RMM tools allows for precise identification of underutilized resources and areas demanding additional support. For example, if an RMM dashboard reveals a consistently low CPU utilization on a particular server, it might suggest that server’s resources are being underutilized, allowing for potential consolidation or reallocation to handle tasks on an overloaded server. Conversely, high error rates on specific applications or devices point to potential areas needing immediate attention and possibly additional resources allocated for troubleshooting and maintenance.
This detailed analysis moves beyond simple guesswork, providing concrete evidence for resource reallocation decisions.
Case Study: Optimizing Server Resources with RMM Data
Imagine a mid-sized company using an RMM platform to manage its IT infrastructure. Their RMM dashboard revealed that two older servers were consistently operating at under 20% capacity, while a newer, more powerful server was frequently overloaded, leading to slowdowns and application failures. By analyzing the historical data from the RMM system, the IT team discovered that the workload on the overloaded server could be easily distributed across the underutilized servers.
This simple reallocation, guided by RMM data, eliminated the performance bottlenecks, preventing costly downtime and improving overall system efficiency. The company also avoided the unnecessary expense of purchasing a new server, saving a significant amount of money.
Measuring the Return on Investment (ROI) of RMM: The Impact Of RMM On Improving IT Team Productivity And Efficiency

Implementing a Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) system is a significant investment, but its potential to boost productivity and efficiency translates directly into a strong return on investment. Understanding how to measure this ROI is crucial for justifying the initial expense and demonstrating its long-term value to stakeholders. This involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) and analyzing how improvements in IT operations translate into tangible cost savings and increased revenue.Calculating the ROI of an RMM system requires a multifaceted approach.
It’s not simply about subtracting costs from benefits; it’s about understanding the qualitative and quantitative impacts on your IT operations. By focusing on specific metrics, you can build a compelling case for the value of your RMM investment.
Key Metrics for Measuring RMM ROI
Several key metrics effectively demonstrate the financial impact of an RMM system. These metrics provide quantifiable data to support the ROI calculation and highlight the system’s contribution to the overall business success. Analyzing these metrics allows for a comprehensive understanding of the RMM system’s effectiveness.
Translating Productivity and Efficiency into Cost Savings and Increased Revenue
Improved productivity and efficiency, facilitated by an RMM system, directly impact the bottom line. Reduced downtime, faster ticket resolution, and proactive maintenance translate into significant cost savings. For example, consider the cost of lost productivity due to system outages. An RMM system’s ability to proactively identify and address potential issues minimizes downtime, thereby reducing these costs. Furthermore, the automation of routine tasks frees up IT staff to focus on higher-value projects, leading to increased revenue generation through improved service delivery and support for strategic initiatives.
Faster resolution times also directly impact customer satisfaction, leading to increased customer retention and potential referrals.
Potential Cost Savings and Benefits of Implementing RMM, The impact of RMM on improving IT team productivity and efficiency
The following table illustrates the potential cost savings and benefits associated with implementing an RMM system. These figures are illustrative and will vary depending on the specific organization, the size of its IT infrastructure, and the chosen RMM solution. However, they provide a realistic overview of the potential financial gains.
| Cost Savings | Benefits | Example/Quantifiable Metric |
| Reduced Help Desk Ticket Costs | Improved Customer Satisfaction | Decrease in average ticket resolution time from 2 hours to 30 minutes, resulting in a 75% reduction in labor costs. |
| Lower Hardware/Software Maintenance Costs | Increased IT Team Efficiency | Reduction in unplanned downtime by 50%, leading to fewer emergency repairs and associated costs. |
| Minimized Downtime Costs | Proactive Problem Prevention | Improved system uptime leading to a 20% increase in employee productivity. |
| Reduced Labor Costs | Enhanced Security Posture | Automation of routine tasks freeing up IT staff for strategic projects, resulting in a 15% reduction in labor costs. |